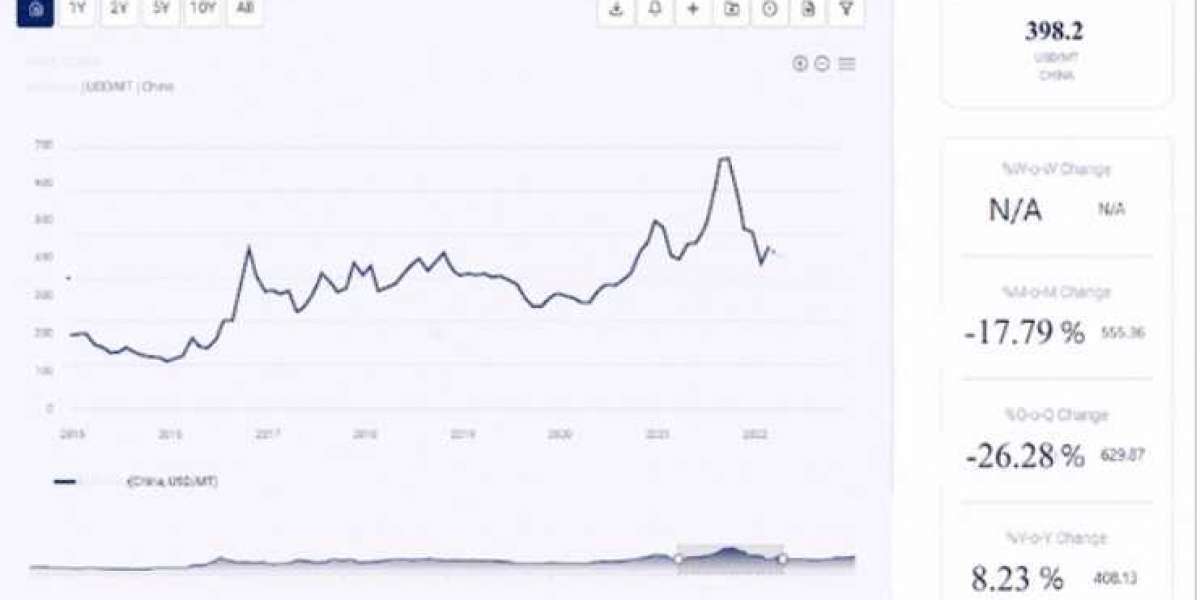
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of the Coffee Price Trend, where we delve into the intricate dynamics of the coffee market, analyze historical price data, and uncover the factors influencing price fluctuations. Coffee, one of the world's most traded commodities, holds a significant place in global culture and economies. In this article, we will navigate through the coffee price trend, gaining insights into market dynamics, trends, and future projections.
Introduction
Coffee is not just a beverage; it's a global phenomenon. From bustling cafes in cosmopolitan cities to remote plantations in tropical regions, coffee's aroma and taste captivate millions of people worldwide. However, behind every cup of coffee lies a complex supply chain influenced by a myriad of factors, including weather conditions, geopolitical events, consumer preferences, and economic trends.
Understanding Coffee
Coffee is derived from the seeds of the Coffea plant, which are roasted and brewed to produce the beverage enjoyed by millions around the world. The coffee market encompasses various types of coffee beans, including Arabica and Robusta, each with its unique flavor profile and growing conditions. Arabica beans, known for their smooth and nuanced flavor, are typically grown at higher altitudes, while Robusta beans, prized for their boldness and caffeine content, thrive in lower altitudes.
Factors Influencing Coffee Price Trend
1. Weather Conditions:
- Weather plays a crucial role in coffee production, with factors such as rainfall, temperature, and sunshine hours directly impacting crop yields and quality. Adverse weather events, such as droughts, floods, or frost, can lead to reduced harvests and supply shortages, driving up coffee prices.
2. Crop Disease and Pests:
- Coffee plants are susceptible to various diseases and pests, including coffee leaf rust and coffee berry borer, which can devastate crops and reduce yields. Outbreaks of crop diseases or pest infestations can disrupt supply chains and lead to price volatility in the coffee market.
3. Global Demand and Consumption Patterns:
- Changes in consumer preferences, lifestyle trends, and economic conditions influence global coffee demand and consumption patterns. Growing demand for specialty coffee, ready-to-drink beverages, and coffee-based products in emerging markets can drive overall coffee consumption and affect prices.
4. Currency Exchange Rates:
- Coffee is traded internationally, with prices denominated in US dollars. Fluctuations in currency exchange rates, particularly in coffee-producing and consuming countries, can impact the competitiveness of coffee exports and imports, affecting market prices.
Request for Real-Time Coffee Prices: https://procurementresource.com/resource-center/coffee-price-trends/pricerequest
Analyzing Coffee Price Trend
1. Historical Price Analysis:
- Analyzing historical coffee price data provides insights into price trends, seasonal patterns, and price cycles. By examining price movements over different time frames, market participants can identify long-term trends and short-term fluctuations, enabling informed decision-making.
2. Market Fundamentals:
- Understanding supply-demand dynamics, production forecasts, inventory levels, and consumption trends is essential for interpreting coffee price trends accurately. Market fundamentals provide valuable insights into the underlying factors driving price movements in the coffee market.
3. Speculative Trading:
- Speculative trading activities, including futures and options trading, can influence short-term price movements in the coffee market. Market sentiment, investor perceptions, and speculative positions play a significant role in determining price direction and volatility.
Future Outlook and Strategies
1. Sustainable Coffee Production:
- Embracing sustainable farming practices, such as shade-grown cultivation, organic farming, and fair trade initiatives, can promote environmentally friendly and socially responsible coffee production. Sustainable coffee sourcing and certification programs ensure ethical practices and support smallholder farmers.
2. Market Diversification:
- Diversifying coffee sources and exploring new origins and varieties can mitigate supply risks and enhance market resilience. Investing in coffee-producing regions with untapped potential and fostering agricultural innovation can create opportunities for growth and diversification.
3. Consumer Education and Innovation:
- Educating consumers about coffee origins, processing methods, and flavor profiles can enhance appreciation for specialty coffee and drive demand for premium offerings. Innovation in coffee brewing techniques, packaging formats, and product differentiation can cater to evolving consumer preferences and lifestyles.
Conclusion
The coffee price trend is shaped by a complex interplay of supply-demand dynamics, weather conditions, market fundamentals, and consumer trends. By understanding these factors and analyzing historical price data, market participants can navigate the coffee market effectively and capitalize on opportunities. Proactive risk management, sustainable practices, and strategic partnerships are essential for ensuring the long-term viability and resilience of the coffee industry in an ever-changing global landscape.